11 Important Signs of Diabetes in Women You Should Know

Last Updated on May 12, 2024 by Lauretta Iyamu, PharmD
When it comes to diabetes, it is important to be aware of the common symptoms and how they vary between men and women. Knowing these symptoms can allow you to detect diabetes earlier and ensure that you take the necessary steps to keep your health in check. In this blog post, we’ll explore the 11 Important signs of diabetes in women – what they are and what you should know about them. Read on to find out more!
Introduction to Diabetes in Women
diabetes in women is a growing epidemic, not just because more women are getting diabetes. Women are more likely to have type 2 diabetes than men, but they also suffer from other symptoms and complications that make it even harder to manage. This article discusses some of the most common signs and symptoms of diabetes in women, including increased energy levels, weight gain, changes in menstrual periods, skin problems, and breathlessness. If you or a loved one is exhibiting any of these signs or symptoms, it’s important to schedule an appointment with your doctor for a diagnosis.
Signs of Diabetes in Women

One of the most common symptoms of diabetes in women is high blood sugar or low blood sugar. If you are a woman experiencing any of the following symptoms, it is very likely that you have diabetes. If you are not sure if you have diabetes, please consult with your doctor.
It’s important to be aware of the signs of diabetes, especially if you are at risk of developing it. Here are 11 signs of diabetes in women:
- Frequent urination: One of the most common signs of diabetes is frequent urination. This is because high glucose levels in the blood can cause the kidneys to work harder to filter it out, leading to more frequent trips to the bathroom.
- Increased thirst: Along with frequent urination, people with diabetes may also feel thirstier because they lose fluids through their urine.
- Hunger: People with diabetes may feel hungry more often, even after eating, because their bodies cannot effectively use the glucose from their food as energy.
- Fatigue: High levels of glucose in the blood can interfere with the body’s ability to use energy, leading to feelings of fatigue or tiredness.
- Blurred vision: Diabetes can cause changes in the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to blurred vision or other vision problems.
- Slow-healing wounds: Diabetes can affect the body’s ability to heal, leading to slower healing of cuts, scrapes, and other wounds.
- Dry skin: Diabetes can cause changes in the body’s ability to produce and retain moisture, leading to dry and darkened skin.
- Numbness or tingling in the hands or feet: High blood glucose levels can damage the nerves, leading to numbness or tingling in the hands or feet.
- Yeast infections: Women with diabetes may be more prone to yeast infections, especially in the vagina.
- High blood sugar levels without any obvious cause.
- Weight gain or difficulty losing weight.
Other signs and symptoms of diabetes include weight loss, decreased sexual desire, nausea and vomiting, blurred vision, and rapid heart rate. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention.
Risk Factors for Developing Diabetes
There are several different types of diabetes, but the most common is called type 2 diabetes. This type of diabetes is often linked to lifestyle factors, and there are certain risk factors that can increase a person’s chances of developing it. Here are some of the main risk factors for developing type 2 diabetes:
- Being overweight or obese: Someone with excess weight, especially around the waist, is more likely to develop type 2 diabetes. Excess fat can make it harder for the body to use insulin, a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar.
- Physical inactivity: If you’re inactive and don’t get enough exercise, you are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes. Exercise helps your body use insulin more efficiently, so being inactive can increase your risk of developing diabetes.
- Family history: If someone has a parent or sibling with type 2 diabetes, they have a higher risk of developing it themselves.
- Age: As a person ages, the risk of developing type 2 diabetes increases. This is especially true for someone over the age of 45.
- Race and ethnicity: Some racial and ethnic groups are at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes, including African Americans, Hispanic Americans, American Indians, Asian Americans, and Pacific Islanders.
- High blood pressure: People with high blood pressure, also known as hypertension, are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes.
- High cholesterol: High cholesterol levels in the blood can increase the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Diagnosing Diabetes in Women

Diagnosing diabetes in women can be difficult because often, there are no specific signs that indicate the disease is present. A doctor will typically take a history of your health and diagnose diabetes based on your clinical presentation and medical history. Additionally, a doctor may run tests to assess blood sugar levels and renal function.
Managing Diabetes With Diet and Exercise

Managing diabetes is important because if you don’t, you can have serious health problems like heart disease, nerve damage, and blindness. But the good news is that there are things you can do to manage your diabetes and feel better. One way is by eating healthy and exercising.
Eating healthy means choosing foods that are good for your body. When you have diabetes, it’s important to eat foods that are high in nutrients and low in sugar, fat, and calories. This can help you keep your blood sugar at a healthy level. Some healthy foods to choose from are:
Fruits and vegetables: These are high in nutrients and low in calories. They can help keep your blood sugar stable and give you energy.
- Whole grains: These are high in fiber, which can help you feel full and keep your blood sugar stable. Examples include whole wheat bread, quinoa, and brown rice.
- Lean protein: This includes foods like chicken, turkey, fish, and tofu. Lean protein can help you feel full and give you energy.
- Healthy fats: These include foods like avocados, nuts, and olive oil. They can help you feel full and give you energy.
Exercise is also important for managing diabetes. When you exercise, your muscles use sugar for energy. This can help lower your blood sugar level. Exercise can also help you lose weight, which is important if you’re overweight and have diabetes. Some ways to exercise are:
- Going for a walk or bike ride
- Swimming
- Playing a sport like basketball or a soccer
- Doing yoga or Pilates
Remember to talk to your doctor before starting any new exercise program.
Managing diabetes with diet and exercise can be hard, but it’s worth it. By eating healthy and exercising, you can feel better and lower your risk of health problems. Always talk to your doctor or a nutritionist for more tips on managing your diabetes.
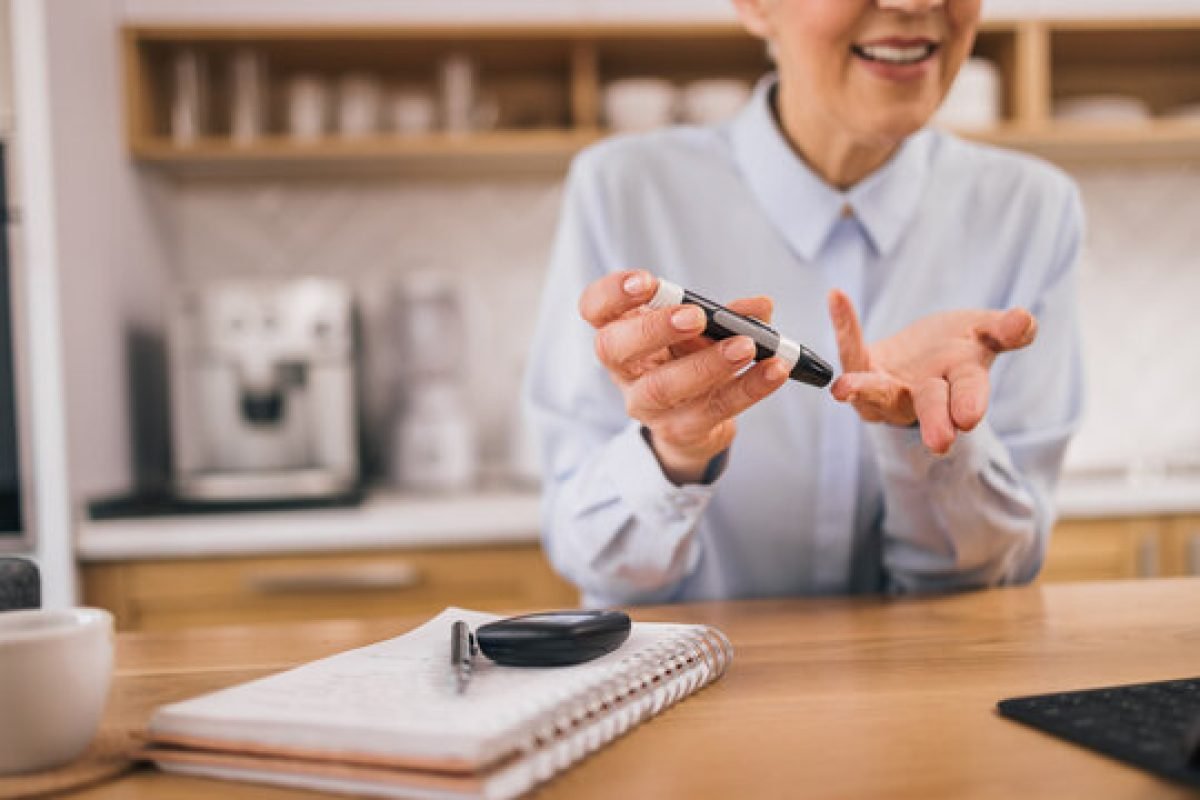
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Blood sugar levels are often monitored in people with diabetes to ensure they remain within a safe range. Monitoring blood sugar levels can also help to detect early signs of diabetes and may even indicate when treatment is necessary. There are several common ways to monitor blood sugar levels in people with diabetes.
Click here to learn how to interpret A1c numbers.
Potential Complications of Diabetes
Diabetes can have several potential complications, including;
- Heart disease
- Stroke
- Kidney failure
- Blindness
Women are particularly at risk for these complications because they often have smaller bodies and less muscle mass than men. Additionally, women are more likely than men to have diabetes due to obesity and hormonal changes.
The Benefits of Early Detection and Treatment
There are many benefits to having diabetes diagnosed and treated early. These include:
- Reduced risk of developing complications such as heart disease, stroke, glaucoma, and kidney failure.
- Improved blood sugar control leads to better overall health and a reduced risk of serious illnesses like cancer.
- Improved mental health (particularly in women with type 2 diabetes), including less depression and anxiety, better cognitive function, and fewer episodes of mild dementia or Alzheimer’s disease.
- Potential delays or prevention of lower limb amputations due to diabetic neuropathy.

Understanding the Link Between Diabetes and Heart Disease
Early Warning Signs
Heart disease is the leading cause of death in women, and according to the American Heart Association (AHA), women are more likely than men to have heart disease as a first sign. Signs and symptoms of diabetes can also contribute to heart disease, including obesity, high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, and insulin resistance. The AHA recommends that people with diabetes monitor their blood sugar levels regularly and talk with their healthcare providers about risk factors for heart disease. Understanding the link between diabetes and heart health may help prevent or delay developing heart disease.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diabetes is a problem with blood sugar levels that can lead to serious health problems. The most common symptom of diabetes is increased urination. While all people with diabetes should get regular checkups, women are especially at risk for these silent killers because they usually have higher rates of other heart disease risk factors, such as obesity and high blood pressure. Early diagnosis and treatment of diabetes can significantly reduce your chances of developing heart disease or stroke.
Long-Term Effects
Heart disease and diabetes are two of the leading causes of death in women. These conditions cause complications that can lead to serious health problems, including blindness, kidney failure, nerve damage, and amputations. In fact, heart disease is the number one killer of women in the United States. Diabetes also significantly impacts female health. Women with type 2 diabetes have a greater risk of developing heart disease than men and are more likely to experience other complications, such as stroke and foot ulcers.
The link between these diabetes and heart disease is complex and multifactorial. However, some key factors contributing to this connection include obesity (especially around the waist), lack of exercise, high blood pressure, unhealthy eating habits (including too much sugar and saturated fat), and a history of heart disease or diabetes in a family member.
There is no cure for heart disease or diabetes, but both conditions can be managed with proper lifestyle choices and treatment. It is important to remember that both conditions are preventable, and early detection and treatment can save lives.
Risk Factors for Women
Heart disease is the number one killer of women in the United States, and diabetes is a major risk factor for heart disease. Diabetes increases the risk of heart disease by increasing the risk of heart attack, stroke, and other cardiovascular problems.
There are many signs and symptoms of diabetes that can be difficult to detect. Some of the most common signs and symptoms of diabetes in women include:
- High blood sugar levels.
- Weight gain.
- Excessive thirst or frequent urination.
- Unusual tiredness or weakness.
- Dizziness or lightheadedness.
- Eye problems, such as vision changes, blindness, or poor vision due to increased eye pressure from high blood sugar levels.
- Numbness or tingling in the hands or feet.
- Poor wound healing.
- Breathlessness.
- Heart problems, such as heart attack, stroke, or heart failure.
Mental Health Considerations for Women with Diabetes
Mental health concerns are not exclusive to those with diabetes but are more common in those with the disease. Diabetes can damage blood vessels and nerves, affecting mood and cognitive functioning. People with diabetes need to seek help for any mental health problems they experience. In addition, social support can be crucial for managing diabetes. People with diabetes should talk to their healthcare providers about any mental health issues they are experiencing and find out what services are available in their area.
Tips for Living Well with Diabetes
. If you have been diagnosed with diabetes, it’s important to take steps to manage the condition and live a healthy, fulfilling life. Here are some tips for living well with diabetes:
- Follow a healthy diet: Eating a healthy diet is important for managing diabetes. This includes eating a variety of whole, unprocessed foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, and limiting sugary drinks and foods. Your healthcare provider or a registered dietitian can help you create a meal plan that is right for you.
- Get regular physical activity: Exercise can help improve your body’s sensitivity to insulin, which can help control your blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, such as brisk walking or cycling, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise, such as running or swimming laps.
- Take your medication as prescribed: If you are prescribed medication to manage your diabetes, it’s important to take it as directed by your healthcare provider. This includes following the prescribed dosage and schedule and not skipping doses.
- Monitor your blood sugar levels: Regularly checking your blood sugar levels can help you and your healthcare provider understand how well your diabetes management plan works and make any necessary adjustments.
- Manage stress: Stress can affect your blood sugar levels, so it’s important to find healthy ways to manage stress, such as through exercise, meditation, or talking to a therapist.
- Get regular check-ups: It’s important to see your healthcare provider regularly to manage your diabetes and prevent complications. This may include regular check-ups, blood tests, and screenings for complications such as eye, kidney, and nerve damage.
- Educate yourself: Learning as much as possible about diabetes can help you make informed decisions about your health and feel more in control of your condition. Talk to your healthcare provider, join a support group, or seek information from reputable sources.
Resources for Further Information
If you’re concerned about the signs of diabetes in women, there are a few resources you can turn to for more information. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) has a website dedicated to diabetes in women, which includes information on the signs and symptoms of diabetes, how to manage the disease, and how to find support. The website also has a section on diabetes care for women, which includes tips on preventing and managing complications associated with diabetes.
If you’re looking for a more general resource on diabetes, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has a website that covers the topic in detail. The website includes information on the causes of diabetes, the types of diabetes, how to diagnose diabetes, and how to manage the disease. It also has a section on diabetes care for women, which includes information on how to prevent and manage complications associated with diabetes.
Living with diabetes can be overwhelming and difficult, but with the right information and support, it doesn’t have to stop you from living a healthy life. Awareness of the common signs and symptoms of diabetes in women is key to early detection and successful management of your condition. By working closely with your doctor, monitoring blood sugar levels regularly, and making lifestyle changes such as eating healthy foods and getting regular physical activity, you can effectively manage your diabetes for years to come.