Diabetes Complications: 5 Surprising Risks You Need to Know

Last Updated on May 12, 2024 by Lauretta Iyamu, PharmD
If you or someone you know has diabetes, it is essential to understand the possible complications this chronic disease can bring. Diabetes can make you sick in many ways, from making you more likely to have a stroke to hurting your nerves. This blog post will discuss the five most common diabetes complications and the steps you can take to reduce your risk. Read on to learn more. Let’s dive in!
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is when the body cannot produce or properly use insulin, a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar. Without insulin, blood sugar levels can become too high, leading to various diabetes complications. These complications can include heart disease, stroke, blindness, kidney failure, and nerve damage.
What are the Complications of Diabetes?
Untreated diabetes can lead to a variety of complications, including:
- Eye problems. Diabetes can cause your eyes to become bloodshot and swollen, leading to vision problems. In addition, if you have diabetes and also have a condition called diabetic retinopathy, which is a complication of diabetes that affects the retina, you may need treatment to prevent blindness.
- Heart disease. Diabetes can increase your risk of heart disease, the leading cause of death in the United States. Diabetes increases your risk of other heart conditions, such as coronary artery disease and heart failure. If you have diabetes, it’s essential to get regular checkups for heart health and to treat any heart conditions that develop.
- Kidney problems. Diabetes can damage your kidneys over time, leading to kidney failure. If you have diabetes and kidney problems, you should get regular checkups and treatment for both conditions.
- Foot ulcers. Diabetes can cause you to develop foot ulcers, which are sores on the bottom of your feet that can be very painful. Foot ulcers are a common complication of diabetes and can be challenging to treat.
- Retinopathy. Diabetes can cause damage to the blood vessels in your retina, which can lead to retinopathy – a complication of diabetes that affects the vision in one or both eyes. If you have retinopathy, you may need treatment to prevent blindness.
1. Eye Complications

One of the most common diabetes complications is an eye disease. Diabetes can cause damage to the blood vessels in the eyes, which can lead to vision problems. In addition, diabetes can also cause the eyes to become dry and irritated. Diabetes can also cause nerve damage in the eyes, leading to vision loss.
There are several ways to prevent or treat diabetes-related eye complications. You can use artificial tears to keep your eyes moist and healthy and over-the-counter eye drops to treat dryness and irritation. If you experience vision problems due to diabetes, talk to your doctor about the best way to treat them. If you are a person with diabetes, you should be especially vigilant about your eye health and should see a doctor if you experience unusual changes in your vision.
2. Foot and Skin Complications
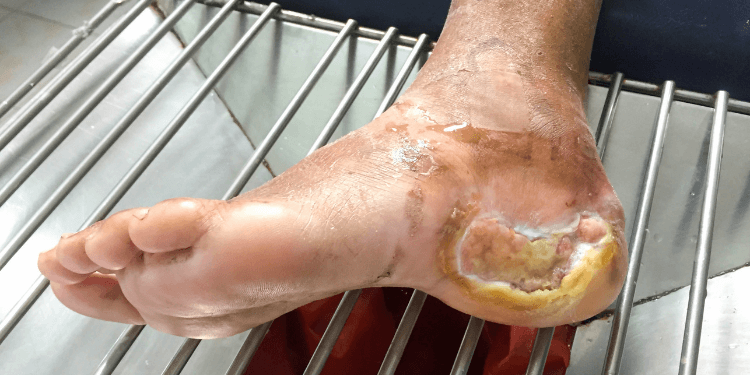
Diabetes can lead to foot and skin complications. Foot complications include:
- Foot pain, often caused by diabetic nerve damage or poor circulation
- Ulcers or sores on the soles of your feet due to less effective treatment of infections or lack of foot care
- Fractures due to improper footwear or accidental falls
- amputations, if diabetes is not controlled
Skin complications include:
Poorly controlled blood sugar levels can lead to problems with your nails and skin. This may cause them to grow too quickly, become brittle and break easily. It can also make you more prone to skin cancer
3. Heart and Blood Vessel Disease

Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the number one killer in the US, accounting for more than a third of all deaths. CVD is caused by atherosclerosis, the thickening and narrowing of blood vessels due to the buildup of fatty materials and foam on the inner walls over time. The most common form is coronary artery disease (CAD), which accounts for about 50 percent of cases. CAD occurs when plaque forms on the inside walls of your coronary arteries, putting you at risk for a heart attack or stroke. Other causes include hypertension, abnormal cholesterol levels, smoking, and diabetes.
4. Kidney Disease

One of the most common complications associated with diabetes is kidney disease. This condition can lead to decreased kidney function and even death if not treated. Other diabetes complications that may lead to kidney problems include:
- Hypertension, or high blood pressure, can damage blood vessels and raise your risk for Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
- Retinopathy (degeneration of the retina) is a complication that can develop after long-term use of oral contraceptives or certain medications, such as ACE inhibitors or angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors
- Acute Kidney Injury (AKI), which is a sudden increase in creatinine levels in the blood due to increased urinary protein intake or some other cause
- Neuropathy, a complication that causes nerve damage and may lead to foot ulcers or kidney transplant
If you have diabetes and signs or symptoms of kidney disease, such as increased blood creatinine levels, talk to your doctor about the best way to manage your diabetes. You may also need to take medications to lower your blood pressure or take other preventive measures to reduce your risk of CKD.
5. Nerve Damage
If diabetes is not well controlled, it can lead to complications such as nerve damage. Diabetes complications can cause several heart and blood vessel diseases. Complications like diabetic neuropathy, a type of nerve damage that can cause numbness and tingling in the hands and feet, can cause nerve damage. This can make it hard to move and feel. Diabetic retinopathy, which is a condition that affects the retina, can lead to blindness.

Importance of Regular Checkups for Diabetics
1. Heart Disease and Stroke
People with diabetes should get regular checkups because the disease and/or treatment can cause problems. Complications can range from mild to life-threatening, so it’s essential to know about them and have regular screenings done by your doctor.
One complication that is especially common in people with diabetes is heart disease. A study found that almost one-third of those with type 2 diabetes develop coronary artery disease within 10 years, compared to only 5% of the general population. Coronary artery disease occurs when plaque builds up inside the arteries leading to the heart, causing angina (pain in the chest) or myocardial infarction (heart attack), both of which can lead to death if not treated quickly.
A second diabetes complication that is commonly associated with heart disease is stroke. Stroke refers to a problem with blood flow to the brain, and it can be caused by many things, such as high blood pressure, atherosclerosis (fatty deposits on the walls of arteries), and diabetes. In fact, type 2 diabetes is the leading cause of stroke in people over 50 years old.
If you have diabetes and are at risk for either coronary artery disease or stroke, you must have regular checkups with your doctor. Understanding your risks will help guide your treatment decisions and protect you from serious complications.
2. Kidney Damage
Regular checkups are essential for people with diabetes, as kidney damage can occur over time. Symptoms of kidney damage may include fatigue, decreased appetite, nausea, and vomiting. If you experience any of these symptoms, make an appointment with your doctor.
Kidney damage can also lead to nerve damage. Nerve damage can cause the hands or feet to feel numb or tingly, make it hard to walk, or make it hard to see or hear. If you experience any of these symptoms, make an appointment with your doctor.
Exercise for Improved Health Outcomes
According to the Centers for Disease Control (CDC), physical activity is vital if you live with diabetes. Exercise recommendations for people with diabetes used to be complicated, but becoming active is not as difficult as you think. There are several benefits of staying active for people with diabetes.
High Blood Pressure
Physical activity benefits overall health and well-being, including reducing the risk of diabetes complications. According to a study published in “Diabetes Care,” people with type 2 diabetes who exercised five days per week had a lower incidence of heart disease, stroke, and death than those who didn’t exercise.
Exercise also helps treat high blood pressure. A Harvard University study found that those who exercised for 30 minutes or more each day had a 15% reduced risk of dying from hypertension, while people who exercised for less than half an hour each day increased their risk by 20%.
Eye Damage
People with diabetes are more likely to have eye problems like diabetic retinopathy. Working out is one of the best ways to reduce your chances of developing these issues. Exercise can help improve blood flow to the eyes, reduce inflammation, and improve vision.
You may like this: Best exercises for diabetes to burn calories quickly.
Diabetes and Stress Management

Stress is a common complication for people with diabetes, as it can lead to higher blood sugar levels and other health problems. There are several ways to reduce stress and manage diabetes symptoms:
- Get enough sleep. Sleep is key for overall health, and people with diabetes need the same amount of sleep as everyone else. On the other hand, sleep deprivation can lead to higher blood sugar levels and other problems, so get enough rest.
- Exercise regularly. Exercise can help reduce stress and improve your overall mood. It also helps control blood sugar levels. Exercise can be done in various ways, including walking, biking, swimming, or lifting weights.
- Eat a balanced diet. A healthy diet can help you manage diabetes symptoms, including reducing blood sugar levels. Make sure to include plenty of fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat foods.
- Meditate or relaxation techniques. Some people find it helpful to learn meditation or relaxation techniques to reduce stress. Others find that simply taking time each day to relax helps them manage their diabetes symptoms better.
- Connect with others who have diabetes. Connecting with other people with diabetes can be a positive source of support and knowledge. Finding support groups and online communities is also a great way to connect with others struggling with the same issues.
Resources Available to Help Fight Against Diabetes
Many different resources are available to help fight against diabetes, including medications and lifestyle changes. While every person is different, following a healthy diet and getting regular exercise can help lower blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of developing diabetes complications. Several wellness programs are also available, such as the National Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP). This program offers proven ways to prevent type 2 diabetes, such as losing weight and increasing physical activity. If you have diabetes, you must speak with your doctor about how to manage your condition.
Wrapping Up
Overall, diabetes is a serious disease that can cause many problems if it isn’t taken care of properly. People with diabetes should get regular checkups and monitor their blood sugar levels to lower their risk of serious complications. In addition, eating well, staying active, dealing with stress, and taking medications correctly are all important ways to improve health and avoid long-term problems caused by diabetes. You can live a healthy life with the right resources and proper management strategies while living with this chronic condition.
References
- Cole JB, Florez JC. Genetics of diabetes mellitus and diabetes complications. Nat Rev Nephrol [Internet]. 2020 Jul [cited 2023 Jan 6];16(7):377–90. Available from: http://www.nature.com/articles/s41581-020-0278-5
- Ceriello A, Prattichizzo F. Variability of risk factors and diabetes complications. Cardiovasc Diabetol [Internet]. 2021 Dec [cited 2023 Jan 6];20(1):101. Available from: https://cardiab.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12933-021-01289-4
- Diabetes symptoms, causes, & treatment | ada [Internet]. [cited 2023 Jan 6]. Available from: https://diabetes.org/diabetes
- Kautzky-Willer A, Harreiter J, Pacini G. Sex and gender differences in risk, pathophysiology and complications of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Endocrine Reviews [Internet]. 2016 Jun 1 [cited 2023 Jan 6];37(3):278–316. Available from: https://academic.oup.com/edrv/article/37/3/278/2354724
- Forbes JM, Cooper ME. Mechanisms of diabetic complications. Physiological Reviews [Internet]. 2013 Jan [cited 2023 Jan 6];93(1):137–88. Available from: https://www.physiology.org/doi/10.1152/physrev.00045.2011
- Jin Q, Ma RCW. Metabolomics in diabetes and diabetic complications: insights from epidemiological studies. Cells [Internet]. 2021 Oct 21 [cited 2023 Jan 6];10(11):2832. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4409/10/11/2832
- CDC. Get active [Internet]. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2022 [cited 2023 Jan 6]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/managing/active.html